Selecting the right PDU voltage is crucial for optimizing server rack performance in data centers. Compatibility with equipment, energy efficiency, and power demands significantly impact operational effectiveness. Data centers consumed up to 400 TWh of energy in 2020, and projections suggest this could quadruple by 2030. High-efficiency options like a 240v PDU or 30 amp PDU 240v ensure scalable, cost-effective solutions. For industries like 240v PDU mining, choosing a PDU 240v setup can maximize power delivery while minimizing energy waste.
Key Takeaways
- Picking the right PDU voltage helps your server racks work well. Check your power needs to choose between 240v or 208v.
- 240v PDUs save more energy and lower costs over time. Use them for powerful computers and data centers needing lots of power.
- 208v PDUs are good for setups with different voltages. They work well in places needing both 120v and 208v power, like in North America.
Overview of 240v and 208v PDUs
Definition of 240v PDU
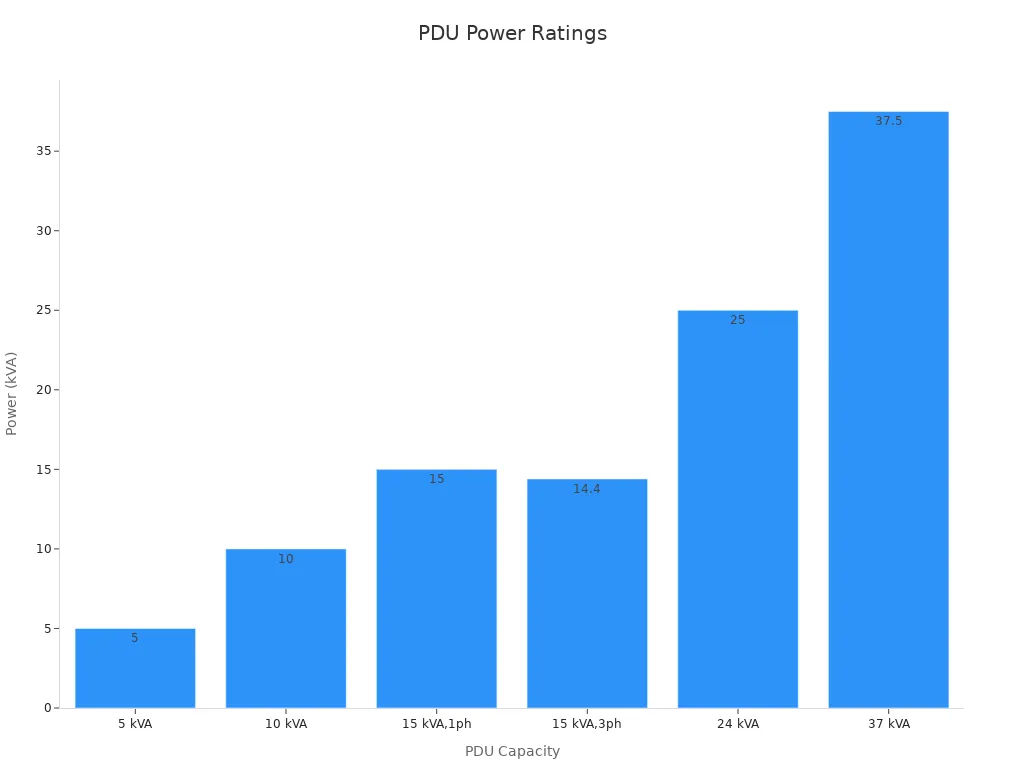
A 240v PDU (Power Distribution Unit) is a device designed to distribute electrical power to multiple servers and IT equipment within a data center. It operates within a voltage range of 200-240 VAC and supports both single-phase and three-phase configurations. These PDUs often feature advanced metering capabilities, enabling precise monitoring of voltage, current, and power consumption. For example, a 240v PDU can handle power ratings ranging from 5 kVA to 37.5 kVA, with outlet configurations such as C13 and C19 to accommodate various equipment needs.
Definition of 208v PDU
A 208v PDU is another type of power distribution unit commonly used in data centers, particularly in North America. It operates at a slightly lower voltage than its 240v counterpart and is often deployed in three-phase configurations. These PDUs are equipped with features such as surge suppression, circuit breakers, and remote monitoring capabilities. They are available in various sizes, including 1U, 2U, and vertical 0U, and support outlet types like C13, C19, and NEMA configurations. The 208v PDU is ideal for environments requiring high power capacity and enhanced safety features.
Common use cases for 240v and 208v PDUs
Both 240v and 208v PDUs serve critical roles in powering server racks and IT equipment. The choice between the two depends on specific use cases:
- 240v PDU: These are ideal for data centers with high power consumption needs, such as those running network storage devices or high-performance computing systems. Their higher voltage allows for improved energy efficiency and reduced power loss.
- 208v PDU: These are commonly used for blade servers and other high-power IT equipment. They support configurations for redundancy and are well-suited for environments requiring both 120v and 208v power.
| Use Case | Voltage | Description |
|---|---|---|
| High Power IT Equipment Racks | 208V | Supports devices like blade servers requiring high power, with configurations for both 120V and 208V. |
| Blade Servers | 208V | Typically use IEC C-19 outlets for high power demands, with configurations for redundancy. |
| Data Center Network/Storage Devices | 240V | Designed to handle high power consumption, often with multiple power supplies for efficiency. |
Key Differences Between 240v and 208v PDUs
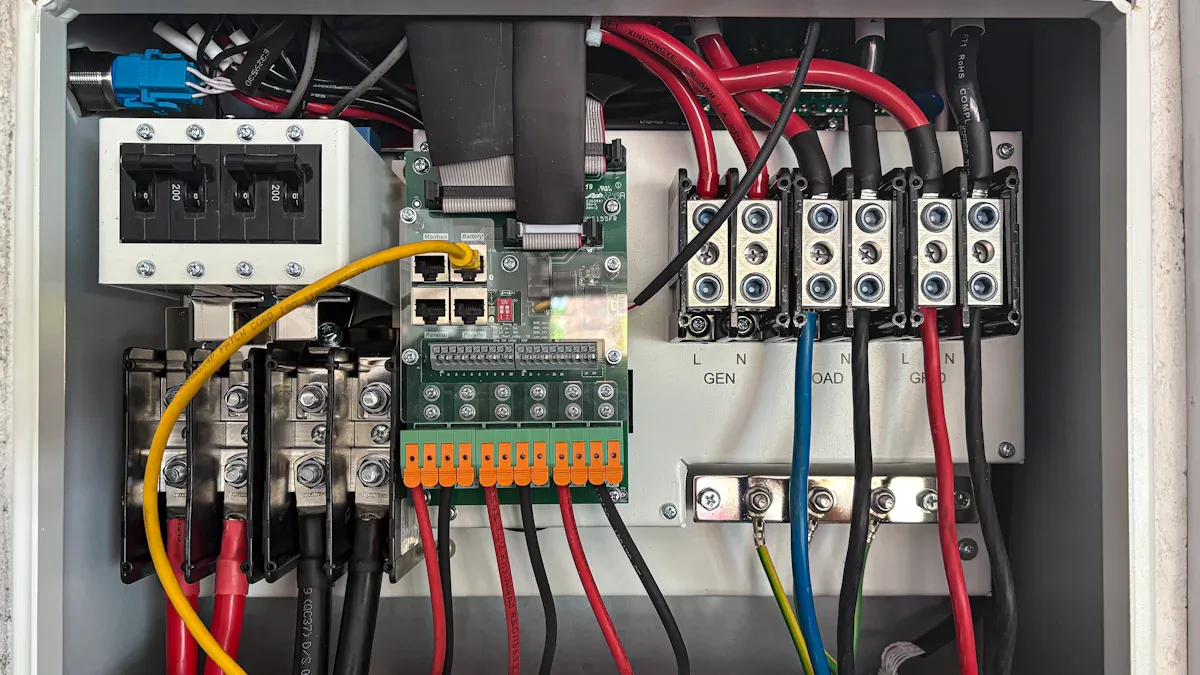
Power delivery and capacity
The power delivery and capacity of a PDU directly influence its ability to support server racks and IT equipment. A 240v PDU provides higher voltage, which translates to greater power capacity. This makes it suitable for high-performance computing systems and data centers with significant energy demands. For example, a 240v PDU can efficiently handle power-intensive tasks like running multiple network storage devices or high-density server racks.
In contrast, a 208v PDU operates at a slightly lower voltage, which may result in reduced power delivery. However, it remains an excellent choice for environments requiring moderate power levels, such as blade servers or mixed-voltage setups. The lower voltage also reduces the risk of overheating, contributing to safer operations in certain scenarios.
| Voltage | Power Capacity | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| 240v | Higher | High-performance computing, storage |
| 208v | Moderate | Blade servers, mixed-voltage environments |
Energy efficiency and operational costs
Energy efficiency plays a critical role in reducing operational costs in data centers. A 240v PDU typically offers better energy efficiency due to its higher voltage. This reduces the current required to deliver the same amount of power, minimizing energy loss during transmission. Over time, this efficiency can lead to significant cost savings, especially in large-scale operations.
On the other hand, a 208v PDU may result in slightly higher energy losses due to its lower voltage. While the difference might seem negligible in smaller setups, it becomes more pronounced in larger data centers. Organizations prioritizing long-term cost efficiency often lean toward 240v PDUs for their superior performance in this area.
Tip: When evaluating energy efficiency, consider the total power consumption of your data center and the potential savings from reduced energy loss.
Compatibility with server equipment
Compatibility with server equipment is a crucial factor when choosing between a 240v and a 208v PDU. Many modern servers and IT devices are designed to operate within a wide voltage range, making them compatible with both options. However, certain high-performance servers and storage systems may perform optimally with a 240v PDU due to its higher power delivery.
Conversely, a 208v PDU is often preferred in North American data centers, where it aligns with standard electrical infrastructure. It also supports mixed-voltage configurations, allowing for the simultaneous use of 120v and 208v equipment. This flexibility makes it a practical choice for diverse IT environments.
Regional availability and data center setups
Regional electrical standards significantly impact the choice between 240v and 208v PDUs. In regions like Europe and Asia, where 240v is the standard voltage, a 240v PDU is the obvious choice. It integrates seamlessly with the existing power infrastructure, ensuring efficient operations.
In North America, 208v PDUs are more prevalent due to the widespread use of three-phase power systems. Data centers in this region often rely on 208v setups to maintain compatibility with local electrical grids. Understanding regional standards is essential for ensuring smooth integration and avoiding potential compatibility issues.
Note: Always consult with a qualified electrician or data center specialist to confirm compatibility with regional power systems.
Pros and Cons of 240v and 208v PDUs
Benefits of 240v PDUs
A 240v PDU offers several advantages for data centers and server racks. Its higher voltage allows for more efficient power delivery, reducing energy loss during transmission. This efficiency translates to lower operational costs over time, making it an ideal choice for facilities with high power demands. Additionally, 240v PDUs support advanced features like intelligent monitoring, which enhances power management and ensures optimal performance.
| Type of PDU | Description |
|---|---|
| Basic (Dumb) PDU | Simple power strips that distribute voltage and current to multiple outlets. |
| Intelligent PDU | Advanced units with monitoring and management capabilities for power usage. |
These features make 240v PDUs particularly suitable for high-performance computing systems and network storage devices.
Drawbacks of 240v PDUs
Despite their benefits, 240v PDUs come with certain drawbacks. Compatibility issues can arise when integrating them into older server racks, often requiring additional hardware like compatibility brackets. Their larger physical form can obstruct ports and rack rails, complicating installation. Furthermore, the size of the cables and plugs may interfere with upper rack spaces, limiting flexibility in some setups.
| Drawback Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Compatibility Issues | Requires additional hardware for older racks. |
| Physical Form Issues | Larger size can obstruct ports and rails. |
| Cable Size Issues | Large plugs may interfere with upper rack spaces. |
Benefits of 208v PDUs
208v PDUs provide flexibility and adaptability in data center environments. They are well-suited for facilities requiring mixed-voltage setups, supporting both 120v and 208v equipment. This versatility is particularly beneficial for data centers handling diverse workloads, including AI applications that demand higher power capacities. The design of triple-output voltage transformers further enhances their adaptability, allowing seamless adjustments to varying power needs.
- Data centers supporting AI workloads may require up to 50 kW per cabinet.
- Global demand for data center capacity is projected to grow by 19%-22% annually through 2030.
- Triple-output voltage transformers enable flexible voltage outputs for diverse IT environments.
Drawbacks of 208v PDUs
While 208v PDUs offer flexibility, they also present challenges. Their total cost of ownership can be high, with electricity accounting for nearly half of annual operating expenses. The average Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) of 2.0 indicates inefficiencies in power usage, which can increase operational costs. Additionally, higher fault current levels necessitate careful circuit protection design to ensure safety. Increased power density at the rack level, while cost-effective, can complicate fault current management.
- Electricity accounts for about 50% of annual operating costs.
- Average PUE of 2.0 highlights inefficiencies in power usage.
- Higher fault current levels require advanced circuit protection.
Choosing the Right PDU for Your Server Racks

Assessing server power requirements
Selecting the right PDU begins with a thorough evaluation of server power requirements. Understanding the total power consumption of all devices within a rack is essential. This ensures that the PDU can handle the load without overloading circuits. Additionally, determining the number of outlets required for all connected devices helps avoid power distribution bottlenecks.
For high-availability applications, redundancy becomes a critical factor. Organizations must evaluate whether dual PDUs or redundant power supplies are necessary to maintain uptime during failures. Remote monitoring and control capabilities also play a vital role in modern data centers, enabling IT teams to track power usage and address issues proactively.
Other considerations include the physical dimensions of the rack and environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity. These factors influence the type of PDU that will integrate seamlessly into the existing infrastructure.
Checklist for Evaluating Server Power Needs:
- Calculate total power consumption for all devices.
- Identify the number of outlets required.
- Assess redundancy needs for critical applications.
- Decide on remote monitoring capabilities.
- Account for rack space and environmental conditions.
Evaluating data center power infrastructure
The power infrastructure of a data center directly impacts the choice of PDU. Facilities must align their PDU selection with the existing electrical setup, including voltage standards and power distribution methods. For instance, data centers in North America often use 208v PDUs due to compatibility with three-phase power systems. Conversely, regions like Europe and Asia favor 240v PDUs, which align with their standard voltage.
Organizations should also consider the configuration of rack PDUs. Intelligent PDUs with load monitoring capabilities can optimize energy efficiency by identifying underutilized resources. Additionally, supplying 400V power minimizes line transmission loss and reduces copper utilization, further enhancing efficiency.
Tip: Evaluate the compatibility of the PDU with the facility’s electrical infrastructure to avoid costly retrofits or operational disruptions.
Considering energy efficiency and costs
Energy efficiency remains a top priority for data centers aiming to reduce operational costs. Studies show that 240v systems often outperform 208v systems in terms of efficiency. The higher voltage reduces current requirements, minimizing energy loss during transmission. Over time, this translates to significant cost savings, particularly in large-scale operations.
Rack PDUs equipped with advanced monitoring features can further enhance efficiency. By tracking power usage under different load conditions, these PDUs enable data centers to optimize energy consumption. Additionally, configurations that support 400V power reduce transmission losses and improve overall performance.
Key Insights on Energy Efficiency:
- 240v systems provide efficiency gains over 208v systems.
- Supplying 400V power minimizes transmission loss and reduces copper usage.
- Intelligent PDUs with load monitoring capabilities optimize energy consumption.
Planning for scalability and future upgrades
Future-proofing the power distribution infrastructure is essential for data centers anticipating growth. Scalable solutions allow facilities to accommodate increasing power demands and higher rack densities without significant overhauls. Modular designs, for example, enable seamless upgrades and expansions as the data center evolves.
Hot-swappable components offer another layer of flexibility. These components can be replaced without downtime, ensuring uninterrupted operations. Additionally, PDUs that support emerging technologies, such as higher power densities and advanced monitoring, prepare data centers for future workloads.
| Strategy/Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Future Expansion and Scalability | Anticipate future growth and select scalable solutions for increasing power demands and rack densities. |
| Modular Designs | Look for designs that allow for seamless upgrades and expansions as the data center evolves. |
| Hot-Swappable Components | Choose components that can be replaced without downtime, enhancing flexibility. |
| Support for Emerging Technologies | Invest in PDUs that accommodate higher power densities and advanced monitoring capabilities. |
| Integration with Cloud Management | Ensure compatibility with cloud-based management platforms for better oversight and control. |
Seeking expert advice if necessary
When in doubt, consulting with experts can simplify the decision-making process. Qualified electricians or data center specialists can provide insights into compatibility, energy efficiency, and scalability. They can also help identify potential challenges and recommend solutions tailored to specific business needs.
Note: Engaging with professionals ensures that the selected PDU aligns with both current requirements and future goals.
Choosing between 240v and 208v PDUs depends on power capacity, energy efficiency, and compatibility. Evaluating server requirements and infrastructure ensures optimal performance.
Tip: Align PDU selection with future scalability goals. Thoughtful planning and expert advice can help businesses maximize efficiency and maintain reliable server rack operations.
FAQ
What is the primary difference between 240v and 208v PDUs?
The main difference lies in voltage levels. A 240v PDU delivers higher voltage, offering greater power capacity, while a 208v PDU supports mixed-voltage setups for flexibility.
Are 240v PDUs compatible with all server equipment?
Not all server equipment supports 240v PDUs. Compatibility depends on the device’s voltage range. Always check equipment specifications before selecting a PDU.
How can data centers improve energy efficiency with PDUs?
Data centers can enhance efficiency by using intelligent PDUs with monitoring features. These devices optimize power usage and reduce energy loss during transmission.
Post time: Apr-20-2025