Selecting the right Smart PDU ensures stable power delivery for every server Pdu and 220v Pdu in a data center. Power failures account for 43% of major outages, so reliable choices matter. The table below compares Pdu Switch and Basic Rack Pdu types for various needs:
| PDU Type | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Basic PDUs | Simple power strips without remote access or monitoring. May include circuit protection. | Budget setups, test environments, stable infrastructures. |
| Metered PDUs | Show real-time power metrics locally to help balance loads and avoid overburdening. | Organizations needing basic power efficiency insights without network connectivity. |
| Monitored PDUs | Provide remote access to power and environmental data, with alerts for threshold breaches. | Critical environments like data centers, finance, healthcare requiring proactive control. |
| Switched PDUs | Allow full remote control of individual outlets, including power cycling and shutdowns. | Multi-site IT operations, remote offices, or unmanned locations needing full control. |
Key Takeaways
- Calculate your total power needs carefully and match the PDU’s voltage and current ratings to your equipment to ensure safe and stable operation.
- Choose a Smart PDU type based on your environment: Metered for basic monitoring, Monitored for detailed tracking, or Switched for full remote control and advanced features.
- Use remote monitoring and environmental sensors to improve uptime, reduce energy costs, and quickly respond to issues without needing on-site visits.
Identify Power and Equipment Requirements
Calculate Power Capacity
Every data center or IT environment must begin with a precise calculation of power capacity. Facility managers should sum the power consumption of all connected devices, typically measured in watts (W) or volt-amperes (VA). This total must not exceed the PDU’s rated capacity. In large-scale environments, power flows from high-voltage transmission lines through transformers and switchgear, eventually reaching low-voltage distribution near IT racks. Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) and automatic transfer switches play a critical role in maintaining uptime during outages. For accurate estimation, teams often use analytical formulas and simulation tools to model different scenarios and refine their calculations. Planning for future growth by including a buffer in the power estimate ensures the infrastructure remains reliable as demands increase.
Check Voltage and Current Ratings
Selecting a Smart PDU requires matching its voltage and current ratings to the local power standards and equipment needs. In the United States, common voltage ratings include 120V and 208/240V, while Europe and Asia typically use 230V. Organizations must also determine whether their setup requires single-phase or three-phase power. The PDU’s maximum load rating should always exceed the combined demand of all connected devices. This approach prevents overloads and supports stable operation. Matching the correct amperage and voltage ensures compatibility and safety for all connected equipment.
Determine Outlet Quantity and Plug Types
The number and type of outlets on a Smart PDU must align with the devices in the rack. Managers should inventory all equipment, noting plug types and power connectors. Some environments require a mix of C13, C19, or other outlet types to accommodate servers, switches, and storage devices. Planning for a few extra outlets supports future expansion and reduces the need for additional PDUs. Careful selection of outlet quantity and plug compatibility streamlines installation and minimizes downtime during upgrades or maintenance.
Select Smart PDU Type and Features

Metered, Monitored, or Pdu Switch
Selecting the right Smart PDU type forms the foundation of efficient power management. Each type offers distinct advantages:
| Feature / Metric | Metered PDUs | Monitored PDUs | Pdu Switch |
|---|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Power Monitoring | Measures voltage, amperage, and current at rack level | Provides detailed energy consumption and environmental data | Adds advanced monitoring plus remote outlet control |
| Outlet-Level Control | Not available | Limited or not available | Enables remote power cycling and sequencing |
| Data Logging & Reporting | Basic consumption data and alerts | Detailed logging and reporting | Comprehensive reporting and API integration |
| Environmental Monitoring | External sensor integration | Integrated sensors in some models | Built-in sensors with environment-aware management |
| Redundancy & Reliability | High reliability, basic redundancy | Similar to metered | Dual power inputs, hot-swappable modules |
| Automation & API Support | Basic | Moderate | Advanced automation and integration |
| Cost of Ownership | Lower | Moderate | Higher, with advanced features |
Organizations often choose a Pdu Switch for remote sites or high-density environments where remote power cycling and advanced monitoring are critical. Monitored PDUs suit facilities that require detailed energy tracking and environmental awareness. Metered PDUs provide essential monitoring for stable, budget-conscious setups.
Real-world deployments show that intelligent PDUs with remote monitoring and outlet-level control can reduce energy costs by up to 15% and improve uptime to 99.99%. These features support proactive management and operational efficiency.
Remote Monitoring and Control
Remote monitoring and control capabilities transform how IT teams manage power infrastructure. With these features, managers can:
- Access real-time data on power consumption, temperature, and humidity from any location.
- Receive instant alerts for threshold breaches, enabling rapid response.
- Remotely power cycle individual outlets using a Pdu Switch, reducing the need for on-site intervention.
A telecommunications company improved equipment uptime by 20% and reduced maintenance costs by monitoring power usage at the outlet level. Remote management features also improve maintenance response times by 40%, minimizing downtime and supporting business continuity.
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Energy Savings | 18% reduction in power consumption, resulting in approximately $120,000 annual savings. |
| Reliability | Proactive alarm thresholds prevented circuit overloads, reducing downtime and extending equipment lifespan. |
| Scalability | Modular design allowed cascading up to ten additional PDUs, supporting infrastructure growth without disruption. |
| Remote Management | Enabled monitoring and control of individual outlets from any location, improving response time and operational control. |
Environmental Sensors and Alerts
Environmental sensors embedded in Smart PDUs monitor temperature, humidity, airflow, and even detect water leaks or dust. These sensors provide real-time alerts, allowing teams to address hazards before they escalate.
- A large retail data center reduced downtime by integrating environmental sensors and intelligent rack PDUs.
- Predictive analytics, powered by sensor data, enable early hazard detection and optimized resource allocation.
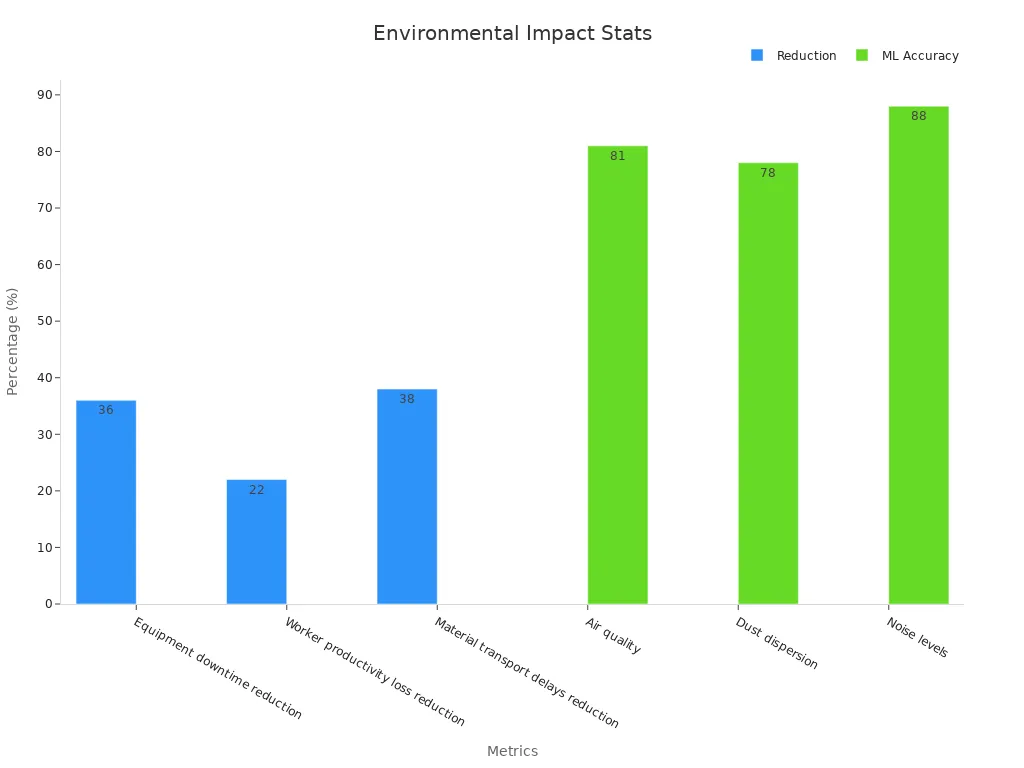
| Metric/Measure | Result/Impact |
|---|---|
| Equipment downtime reduction | 36% decrease after implementing dust and noise control measures enabled by IoT sensors |
| Worker productivity loss reduction | 22% decrease due to quieter work environment |
| Material transport delays reduction | 38% decrease attributed to improved air quality and reduced dust buildup |
| Machine learning model accuracy | 81% (air quality), 78% (dust dispersion), 88% (noise levels) supporting real-time interventions |
| Data volume for analysis | ~129,600 raw sensor readings collected over 12 months |
These statistics highlight the value of environmental monitoring in reducing downtime and improving operational efficiency.
Security and Access Management
Modern Smart PDUs must protect critical infrastructure from cyber threats and unauthorized access. Security and access management features include:
- Role-based access control and multi-factor authentication.
- Strong encryption for data at rest and in transit.
- Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments.
- Incident response plans for rapid threat mitigation.
A survey of IT managers reported a 40% improvement in maintenance response times in data centers using remote monitoring services. Switched PDUs, such as a Pdu Switch, enable remote control of individual outlets, reducing downtime and improving operational efficiency. Enhanced security features also minimize human intervention, protecting sensitive infrastructure and supporting compliance with industry standards.
Scalability and Future-Proofing
Scalability and future-proofing ensure that Smart PDUs can adapt to evolving business needs and technology trends. Key considerations include:
- Modular and scalable architectures that support easy expansion.
- Integration with IoT and AI for predictive maintenance and advanced analytics.
- Compatibility with renewable energy sources and evolving data center designs.
- Support for virtualization and software-defined infrastructure.
Smart PDUs with modular designs allow organizations to cascade additional units as their infrastructure grows. Enhanced monitoring and analytics capabilities enable real-time data analysis and energy optimization, supporting large-scale deployments. The trend toward flexible, scalable PDU systems ensures adaptability to new technologies and future requirements.
Smart PDUs designed for scalability and future-proofing help organizations align with sustainability goals, optimize energy usage, and maintain operational efficiency as their infrastructure evolves.
Installation and Compatibility Considerations

Mounting Options and Form Factor
Selecting the right mounting option and form factor ensures a smooth installation and optimal use of rack space. Smart PDUs offer several mounting styles, each designed for specific environments. Horizontal rack-mounted PDUs fit standard 19-inch racks and support efficient power sharing. Vertical (0U) PDUs maximize space by mounting along the rack’s side, while floor-mounted units handle high-density power needs in large facilities. Cabinet-mounted PDUs protect sensitive devices and integrate environmental sensors for added safety. Portable PDUs provide flexibility for temporary setups. The table below summarizes key mounting options:
| Mounting Option | Typical Use Case | Key Features and Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Rack-mounted PDUs | Server racks | Compact, reliable, support load balancing and energy saving |
| Floor-mounted PDUs | High-density facilities | Handle heavy loads, ensure smooth power delivery |
| Cabinet-mounted PDUs | Enclosed spaces | Surge protection, environmental monitoring |
| Portable PDUs | Mobile or temporary setups | Flexible, easy to move, reliable power |
Integration with Existing Infrastructure
Smart PDUs integrate seamlessly with modern data center and industrial environments. They support IP aggregation, allowing multiple units to operate under a single IP address, which reduces deployment complexity. Integration with environmental sensors enables real-time monitoring of heat and humidity within racks. Remote connectivity through network or serial interfaces allows administrators to manage power and configure alerts from anywhere. Compatibility with DCIM software provides centralized access to power and environmental data. Features like alternating and locking outlets improve cable management and secure connections, while modular designs allow upgrades without full replacement.
- Smart PDUs support remote monitoring and configuration.
- Integration with DCIM systems enables comprehensive facility management.
- Modular features simplify upgrades and future-proof infrastructure.
Physical and Network Compatibility
Physical and network compatibility play a critical role in Smart PDU selection. Leading models offer vertical rack mounting, tool-less installation, and low-profile designs to fit diverse rack systems. They support a range of voltages and currents, including single-phase and three-phase power, and feature color-coded circuit breakers for safety. Network management protocols such as HTTP, HTTPS, SSH, and SNMP ensure secure and flexible connectivity. Daisy chaining allows up to 64 PDUs on a single network chain, reducing the need for additional ports. Advanced units provide gigabit Ethernet, wireless connectivity, and open APIs for integration with DCIM and BMS software. These features guarantee reliable operation and easy integration with existing IT and power infrastructure.
Evaluate Energy Efficiency, Reliability, and Cost
Energy Monitoring and Reporting
Smart PDUs deliver real-time energy monitoring and advanced reporting features. These devices track power consumption at both the rack and outlet levels, providing actionable data for IT managers. Environmental sensors, such as temperature and humidity monitors, help optimize energy use and maintain equipment reliability. Remote on/off switching and outlet-level control further improve energy management, reducing manual intervention and operational costs. Advanced analytics and IoT integration support proactive decision-making, allowing teams to identify inefficiencies and optimize power distribution.
- Real-time monitoring enables quick detection of abnormal power usage.
- Environmental sensors maintain optimal rack conditions.
- Remote management reduces the need for on-site maintenance.
Smart PDUs with these capabilities help organizations achieve energy savings and support sustainability goals.
Build Quality and Redundancy
High-quality Smart PDUs meet strict industry certifications and redundancy standards. The following table highlights key certifications that validate manufacturing consistency, safety, and environmental compliance:
| Certification | Purpose |
|---|---|
| ISO9001 | Ensures consistent manufacturing processes for quality |
| UL | Guarantees compliance with electrical safety standards |
| RoHS | Addresses environmental impact and safety |
| CE | Ensures compliance with health and safety regulations |
| VDE | Validates electrical safety and performance |
Redundancy features, such as dual-power inputs and network failover, ensure continuous operation. Modular designs and overload protection enhance reliability and support future growth. Leading Smart PDUs also offer locking outlets and scalable architectures for added safety and adaptability.
Total Cost of Ownership
Evaluating the total cost of ownership (TCO) involves more than just the initial purchase price. Organizations must consider acquisition, operational, downtime, and disposal costs. Features like hot-swappable components, remote management, and scalability reduce downtime and lower long-term expenses. Security measures, such as encryption and role-based access control, protect infrastructure and minimize risk. Testing and validation procedures, including simulated peak load tests and compatibility checks, ensure reliable performance before deployment. A structured checklist that assesses power requirements, scalability, monitoring, compatibility, energy efficiency, security, and TCO helps organizations make informed decisions and maximize return on investment.
Practical Checklist and Comparison Table
Feature Comparison Table
Selecting the right Smart PDU involves comparing key features across different types. The table below summarizes the main options and their best use cases:
| PDU Type | Description | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Basic PDUs | Simple power strips without remote access or monitoring. May have circuit protection. | Budget setups, test environments, stable infrastructures |
| Metered PDUs | Show real-time power metrics locally to help balance loads. | Organizations needing basic power efficiency insights without network connectivity |
| Monitored/Smart PDUs | Provide remote monitoring and control, environmental sensors, and alerts. | Data centers requiring remote management and environmental monitoring |
| Switched PDUs | Allow remote outlet-level control and rebooting. | Environments needing granular control and remote reboot capabilities |
| ATS (Automatic Transfer Switch) | Automatically switch power sources to maintain uptime. | Critical systems requiring power redundancy and failover |
| Hot-Swap PDUs | Support replacement without downtime. | High-availability environments needing maintenance without interruption |
A remote server room can avoid costly downtime by using a Smart PDU. The team remotely reboots a switch, resolving issues in minutes. Environmental sensors also send alerts if temperatures rise, preventing hardware damage.
Scoring and Shortlisting
A structured checklist helps teams evaluate and compare Smart PDUs efficiently. Key criteria include:
- Power capacity and voltage compatibility
- Installation and mounting options
- Monitoring and remote control features
- Breaker and surge protection
- EMI filters for interference reduction
- Built-in display or control boards
- Brand reliability, MTBF, and warranty
- Integration with SNMP, HTTP, or Telnet protocols
- Compatibility with DCIM platforms
- Environmental sensors for temperature and humidity
Teams can assign scores to each criterion based on project needs. Shortlisting becomes easier when each PDU is rated against these factors. This approach ensures the final selection aligns with operational goals and infrastructure requirements.
Selecting the right Smart PDU depends on understanding equipment needs and matching features like remote monitoring or a Pdu Switch. A structured, step-by-step approach helps organizations avoid costly mistakes. Teams should use the checklist to compare options and make confident, informed decisions for their power infrastructure.
FAQ
What is the difference between a Basic PDU and a Smart PDU?
A Basic PDU distributes power without monitoring or control. A Smart PDU offers remote management, energy monitoring, and advanced features for critical environments.
How does remote monitoring benefit data center operations?
Remote monitoring allows teams to track power usage, receive alerts, and control outlets from anywhere. This improves uptime and reduces the need for on-site maintenance.
Can Smart PDUs support future expansion?
Yes. Many Smart PDUs feature modular designs and scalable architectures. These allow organizations to add capacity or integrate new technologies as needs change.
Post time: Jun-24-2025