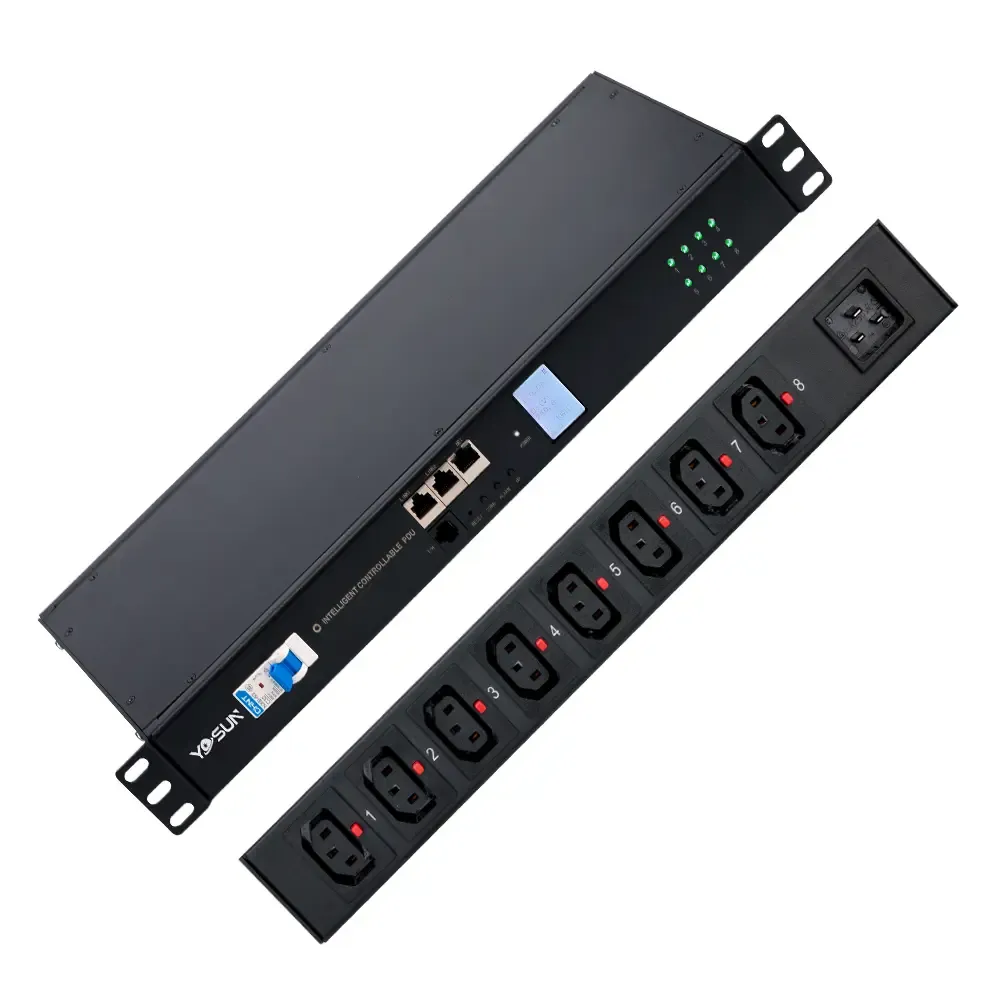
Data centers continue to face power-related outages, with rack PDUs playing a major role in these incidents. Operators reduce risks by choosing a horizontal rack PDU with overload protection, surge suppression, and redundant inputs. Manufacturers now offer intelligent PDUs with outlet-level monitoring, remote management, and energy-saving features. These tools help teams track power usage, receive alerts, and act quickly. Routine inspections, real-time monitoring, and high-quality materials, such as aluminum alloy, further boost reliability and extend equipment life.
Key Takeaways
- Perform regular visual inspections monthly to catch loose cables, dust, and damage early.
- Check and reset breakers carefully after finding and fixing the cause of trips to avoid repeated outages.
- Use PDUs with real-time monitoring and remote management to track power use and respond quickly to alerts.
- Balance power loads across outlets to prevent overloads, reduce downtime, and extend equipment life.
- Keep firmware updated to improve security, fix bugs, and maintain stable PDU operation.
Critical Maintenance for Horizontal Rack PDU Reliability

Routine Visual Inspections and Physical Checks
Regular inspections help keep power systems running smoothly. Technicians should look for loose cables, damaged outlets, and signs of overheating. Dust and debris can build up inside racks, so cleaning the area around the PDU prevents airflow problems. Checking the aluminum alloy housing for dents or cracks ensures the unit stays strong and safe. Many teams use a checklist to make sure they do not miss any steps during inspections.
Tip: Schedule inspections at least once a month. This habit helps catch small issues before they become big problems.
Breaker Status and Reset Procedures
Circuit breakers protect equipment from overloads and faults. Staff should check breaker positions during each inspection. If a breaker trips, they must find the cause before resetting it. Overloaded circuits, faulty devices, or short circuits often cause trips. Resetting a breaker without fixing the problem can lead to repeated outages. Teams should label each breaker clearly, so they know which outlets connect to which devices.
A simple reset procedure includes:
- Identify the tripped breaker.
- Unplug or power down connected equipment.
- Inspect for visible faults or overloads.
- Reset the breaker by switching it off, then on.
- Restore power to equipment one device at a time.
This process helps prevent further damage and keeps the horizontal rack PDU operating safely.
Monitoring LED Indicators and Display Panels
LED indicators and display panels give real-time feedback on power status. Green lights often show normal operation, while red or amber lights warn of problems. Intelligent display panels show load levels, voltage, and current. Staff can spot early signs of trouble by watching for abnormal values, such as voltage outside safe limits or sudden changes in current. These readings help detect issues before they cause equipment failure.
Display panels on modern horizontal rack PDUs allow users to monitor connected equipment continuously. If the system detects unsafe conditions, it can alert staff or even shut down outlets to prevent damage. This proactive approach supports reliable power management and reduces downtime.
Verifying Outlet Settings and Load Balancing
Proper outlet settings and balanced power loads are essential for safe and efficient operation in any data center. Technicians who follow best practices can prevent overloads, reduce downtime, and extend equipment life. Here are the recommended steps for verifying outlet settings and ensuring load balancing in a horizontal rack PDU:
- Assess the power requirements of all connected devices and check the input ratings of the PDU, such as 10A, 16A, or 32A. Select the correct power cords and connectors for each device.
- Use PDUs with monitoring or metering capabilities to view real-time power consumption. Metered PDUs provide alerts and historical data, helping staff make informed decisions.
- Monitor load levels to avoid overloading any single outlet or circuit. Metered PDUs can alert staff before a breaker trips, allowing for proactive load distribution.
- Choose PDUs with outlet-level metering for detailed tracking of each device’s power usage. This helps identify which devices draw the most power and may need to be moved.
- Use PDUs with switching functions to remotely turn outlets on or off. This feature allows for remote reboots and reduces the need for on-site intervention.
- Distribute power loads evenly across all available phases by staggering outlet groupings. This approach simplifies cabling and improves reliability.
- Monitor environmental factors like temperature and humidity using sensors connected to the PDU. Maintaining proper conditions helps prevent equipment failure.
Note: Uneven power distribution can cause hazards such as fires, equipment damage, and tripped breakers. Proper load balancing ensures a stable power supply, prevents overloads, and supports business continuity. When power is not balanced, the risk of downtime and hardware failure increases.
Using Built-In Diagnostic Tools
Modern horizontal rack PDUs come equipped with advanced diagnostic tools that help technicians maintain system health and prevent failures. The following table outlines common built-in diagnostic features and their uses:
| Diagnostic Tool / Feature | Description / Use in Maintenance |
|---|---|
| Real-time Power Monitoring | Tracks voltage, current, and load balance to detect anomalies early and maintain optimal power distribution. |
| Environmental Sensors | Monitor temperature and humidity; trigger alerts to prevent overheating and hardware damage. |
| Built-in Display / Control Board | On-site LCD/OLED panels provide immediate visibility into power usage and system health. |
| Alert Systems | Set thresholds and receive notifications for abnormal conditions, enabling proactive maintenance. |
| Remote Management Capabilities | Allows rebooting unresponsive devices remotely, reducing downtime and need for physical intervention. |
| Protocol Integration (SNMP, HTTP, Telnet) | Enables integration with network and DCIM platforms for comprehensive infrastructure monitoring and control. |
| Breaker and Surge Protection | Protects hardware from electrical faults, contributing to system reliability and maintenance. |
Technicians benefit from these diagnostic tools in several ways:
- They receive real-time power quality metrics at both the inlet and outlet levels, which helps detect voltage sags, surges, and current spikes.
- Waveform capture during power events helps identify the root cause of failures, such as current surges from faulty power supplies.
- Tracking minimum and maximum power values over time allows staff to spot patterns that may lead to critical failures.
- Outlet-level monitoring can detect idle or malfunctioning devices, supporting predictive maintenance.
- These tools provide continuous monitoring without the need for external meters, making maintenance more efficient.
- Access to both historical and real-time data supports better decision-making and helps optimize uptime.
Post time: Jul-24-2025