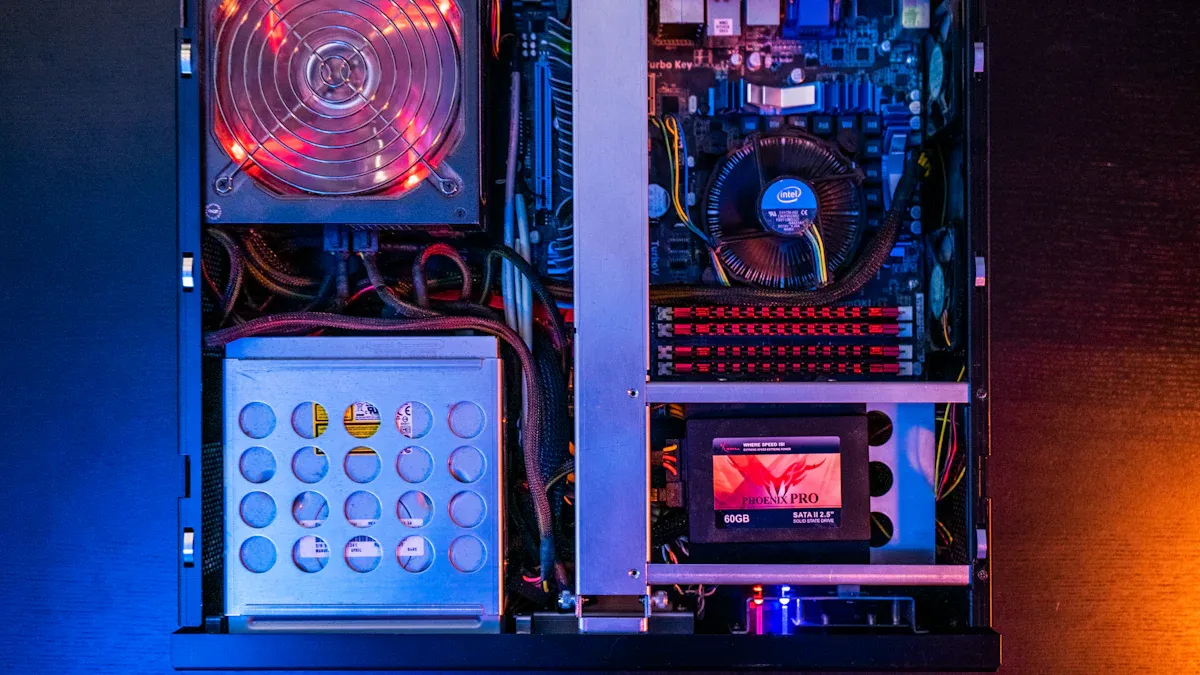
Power Distribution Units (PDUs) and Power Supply Units (PSUs) play vital roles in modern power management systems. PDUs distribute electricity across multiple devices, ensuring organized and efficient power flow. PSUs convert electrical energy into usable formats for individual devices. In data centers, PDUs like the horizontal rack PDU improve airflow and reduce cable clutter, while PSUs deliver reliable power to IT equipment.
Key Takeaways
- PDUs share power to many devices, keeping energy balanced and safe.
- PSUs change strong AC power into weaker DC power for devices.
- Combining PDUs and PSUs improves power use in data centers, saving energy and reducing breaks.
What is a PDU?
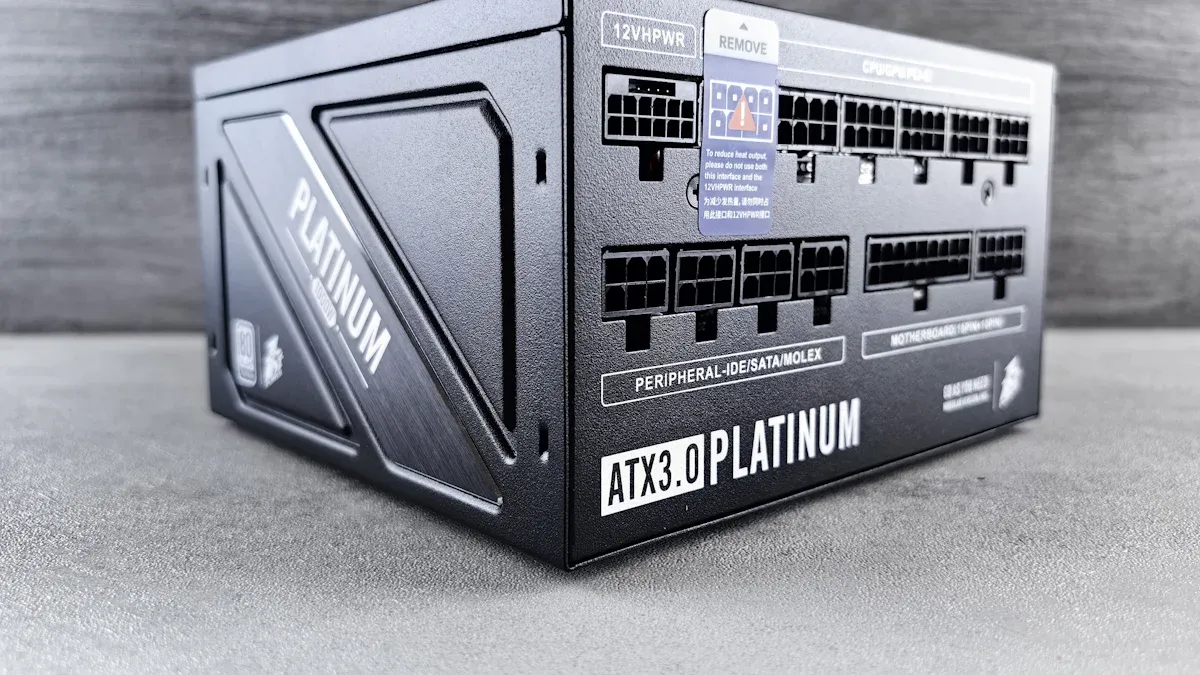

Definition and Purpose
A Power Distribution Unit (PDU) is a device designed to distribute electrical power from a single source to multiple devices. It plays a critical role in environments like data centers, where numerous servers and IT equipment require reliable power. PDUs ensure smooth operations by balancing electrical loads and preventing equipment damage. They also contribute to energy efficiency, which is increasingly vital as technology evolves.
PDUs act as the backbone of power management systems, ensuring that electricity flows safely and efficiently to connected devices.
Key Features of a PDU
Modern PDUs come equipped with advanced features that enhance their functionality and reliability.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Environmental Monitoring | Tracks temperature and humidity to protect critical IT infrastructure. |
| Hot Swappable | Allows updates and repairs without interrupting operations. |
| Optimized Cable Management | Reduces hazards and inefficiencies through features like U-Lock outlets. |
| Remote Connectivity | Enables remote monitoring and configuration, improving response times. |
| Outlet Control | Provides proactive monitoring and management of connected devices. |
These features make PDUs indispensable for maintaining operational efficiency and preventing downtime in high-demand environments.
Applications in Data Centers and IT Environments
PDUs are essential in data centers, IT rooms, and networking setups. They distribute power to servers, routers, and switches while offering remote reboot capabilities. In addition to powering devices, PDUs help monitor energy usage and environmental conditions. This functionality aids in conserving energy and optimizing operations. By ensuring even power distribution, PDUs prevent overloads and extend the lifespan of connected equipment.
Horizontal Rack PDU: A Common Type
Horizontal rack PDUs are among the most widely used types in data centers. These PDUs fit seamlessly into standard 19-inch racks, making them ideal for organized power distribution. They improve cable management and airflow, reducing clutter and enhancing cooling efficiency. Smart horizontal rack PDUs also monitor energy consumption in real-time, helping identify inefficiencies and reduce operational costs. Their ability to power down idle equipment during non-peak hours further supports energy conservation efforts.
What is a PSU?
Definition and Purpose
A Power Supply Unit (PSU) is a critical component in electronic systems, responsible for converting and regulating electrical power. It transforms high-voltage alternating current (AC) from mains electricity into low-voltage direct current (DC) required by internal components. This ensures stable and consistent power delivery to devices like motherboards, CPUs, RAM, and storage drives.
PSUs adhere to industry standards that define their role and compatibility. For desktop PCs, ATX12V standards specify connector designs and power requirements. Servers rely on EPS12V standards, which impose stricter electrical specifications to meet higher performance demands. Built-in protection features safeguard systems against power surges and electrical faults, enhancing reliability and preventing damage.
Key Features of a PSU
Modern PSUs incorporate advanced technologies to optimize performance and efficiency.
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Active Efficiency | Measures power conversion effectiveness during standard operations at varying loads. |
| Standby Power Consumption | Reduces energy waste when the PSU is idle, supporting eco-friendly practices. |
| Annual Operating Cost | Evaluates financial impact based on energy consumption, aiding cost-effective decision-making. |
Reliability metrics like Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) and Mean Time To Failure (MTTF) further highlight the durability of PSUs, ensuring long-term functionality in demanding environments.
Applications in Electronic Devices and Systems
PSUs are indispensable in computers, gaming consoles, and industrial equipment. They power high-performance computing systems, enabling tasks like online gaming, streaming, and data processing. The global PSU market, valued at USD 2.5 billion in 2023, is projected to grow to USD 4.8 billion by 2032, driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for efficient power solutions. Their role in maintaining operational stability makes them a cornerstone of modern electronics.
Comparing PDU and PSU
Functionality: Distribution vs. Conversion
PDUs and PSUs serve distinct purposes in power management systems. PDUs focus on distributing electrical power to multiple devices, ensuring balanced and efficient energy flow. In contrast, PSUs convert high-voltage alternating current (AC) into low-voltage direct current (DC), which is essential for powering individual electronic components.
A comparison of their functionality highlights these differences:
| Feature | Digital Electricity™ | Digital Current™ |
|---|---|---|
| Power Delivery | Discrete energy packets with safety checks | Continuous DC power delivery |
| Distance Capability | Longer distances without voltage drop | Standard cable lengths |
| Voltage Distribution | Up to 450 volts DC | DC power along cables |
| Line Losses | Reduced due to no capacitive/inductive loss | Standard line losses |
PDUs excel in environments like data centers, where they distribute power to servers and networking equipment. PSUs, on the other hand, are integral to devices such as computers and gaming consoles, where stable power conversion is critical for performance.
Physical Design and Placement
The physical design and placement of PDUs and PSUs reflect their unique roles. PDUs, such as the horizontal rack PDU, are designed to fit seamlessly into server racks. This design optimizes cable management and airflow, reducing clutter and improving cooling efficiency. Horizontal rack PDUs are particularly popular in data centers due to their compact and organized layout.
PSUs, however, are built to integrate directly into electronic devices. Their compact size and internal placement ensure they remain unobtrusive while delivering reliable power. For example, a PSU in a desktop computer resides within the case, converting AC power from the wall outlet into DC power for internal components.
The placement of these devices also influences their accessibility. PDUs are often mounted externally for easy monitoring and maintenance, while PSUs are enclosed within devices, prioritizing functionality over accessibility.
Role in Power Management
PDUs and PSUs play complementary roles in power management. PDUs ensure efficient power distribution across multiple devices, preventing overloads and optimizing energy usage. Advanced PDUs monitor environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, to protect connected equipment.
PSUs, on the other hand, focus on delivering stable and regulated power to individual components. Their role in converting and regulating power ensures the longevity and performance of electronic devices. Built-in protection features, such as surge protection and overcurrent safeguards, enhance their reliability.
The adoption of PDUs and PSUs varies across regions based on infrastructure and energy needs. For instance:
| Region | Trend Description | Key Factors Influencing Demand |
|---|---|---|
| North America | Increased demand for high-density PDUs due to data consumption from cloud providers | Energy efficiency standards, energy consumption of data centers (2% of U.S. electricity), modular PDUs adoption |
| Asia-Pacific | Demand driven by infrastructure development and energy costs | Advanced PDUs for grid stability, cost-effective solutions in India, surge protection for voltage fluctuations |
| Europe | Sustainability focus leading to renewable energy integration in PDUs | EU Climate Neutral Data Centre Pact, demand for liquid-cooled PDUs in warmer climates, energy efficiency regulations |
These trends highlight the evolving role of PDUs and PSUs in addressing global energy challenges. Together, they form the backbone of modern power management systems, ensuring reliability and efficiency in diverse applications.
How PDUs and PSUs Work Together
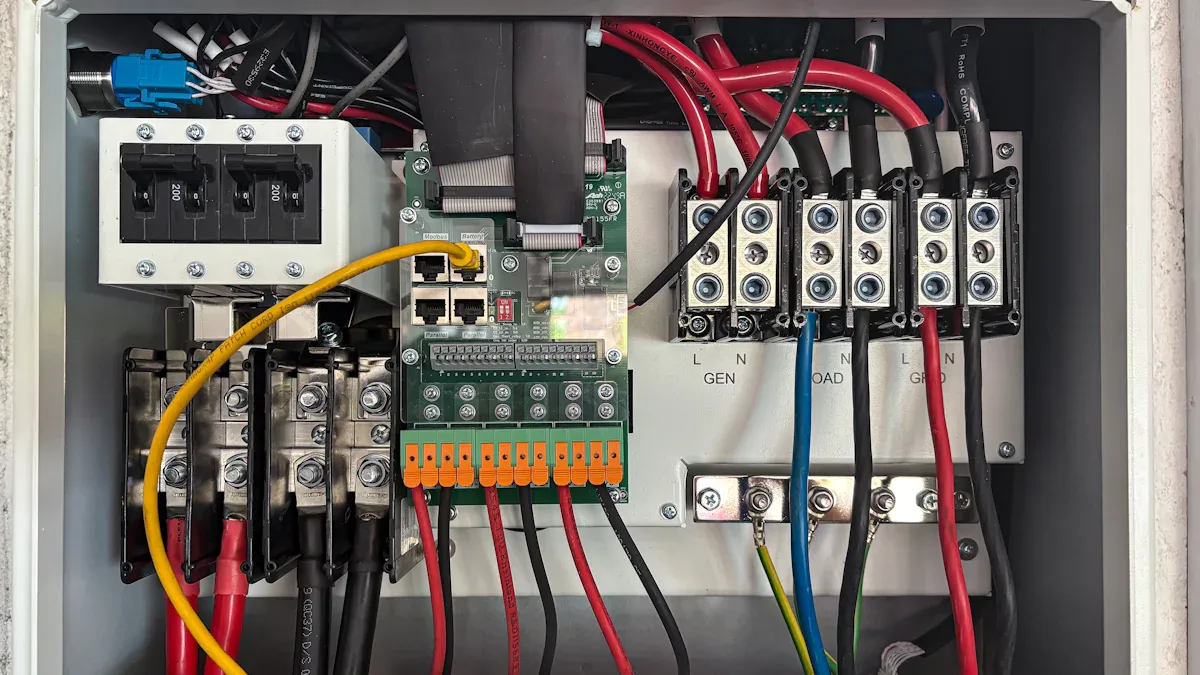
Integration in Data Centers
PDUs and PSUs form a critical partnership in data centers, ensuring seamless power management. PDUs, such as the horizontal rack PDU, distribute power efficiently across server racks, while PSUs convert this power into usable formats for individual devices. This integration supports the high energy demands of modern IT infrastructure.
Data centers often rely on intelligent PDUs to monitor power usage and environmental conditions. These devices provide real-time data, enabling administrators to identify inefficiencies and optimize energy consumption. PSUs complement this by delivering stable power to servers, preventing disruptions caused by voltage fluctuations. Together, they create a robust system that minimizes downtime and maximizes operational efficiency.
Ensuring Reliable Power Delivery
Reliable power delivery is essential for maintaining uninterrupted operations in critical environments. PDUs and PSUs work together to achieve this goal by addressing different aspects of power management. PDUs ensure even distribution of electricity, preventing overloads and protecting connected equipment. PSUs, on the other hand, regulate and stabilize the power supply, safeguarding sensitive components from damage.
The financial advantages of this collaboration are significant. Intelligent PDUs provide visibility into power quality data, helping optimize energy consumption. Identifying power-related issues early can prevent costly downtime, which accounts for 44% of outages. By reducing downtime and improving energy efficiency, data centers can achieve substantial cost savings.
| Benefit Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Power Usage Optimization | Intelligent PDUs provide visibility into power quality data, helping to optimize energy consumption. |
| Downtime Prevention | Identifying power-related issues can prevent costly downtime, which accounts for 44% of outages. |
| Cost Savings | Reducing downtime and optimizing power usage leads to significant financial savings for data centers. |
This synergy between PDUs and PSUs ensures that power delivery remains consistent, efficient, and cost-effective.
Real-World Examples of Combined Use
The integration of PDUs and PSUs can be observed in various real-world scenarios. In large-scale data centers, horizontal rack PDUs distribute power to multiple servers within a single rack. Each server contains a PSU that converts the distributed power into the specific voltage required for its components. This setup ensures that all devices receive the energy they need without overloading the system.
Another example is in cryptocurrency mining operations, where high-performance computing equipment demands substantial power. PDUs distribute electricity to mining rigs, while PSUs regulate the power supply to prevent overheating and ensure stable performance. This combination supports the continuous operation of mining equipment, which is critical for profitability.
In smaller IT environments, such as office server rooms, PDUs and PSUs work together to maintain reliable power delivery. PDUs manage the distribution of electricity to networking equipment, while PSUs ensure that devices like routers and switches operate without interruption. This collaboration enhances productivity and reduces the risk of equipment failure.
The partnership between PDUs and PSUs demonstrates their complementary roles in power management. By working together, they provide a foundation for reliable, efficient, and scalable energy solutions.
Choosing the Right Solution
Factors to Consider
Selecting the right power management solution requires evaluating several critical factors. Each environment has unique requirements that influence the choice between a PDU and a PSU.
- Scalability: PDUs must support future growth by accommodating new devices and increased power demands.
- Capacity: Higher capacity prevents overloading as equipment is added to the system.
- Configuration Flexibility: Adaptable designs allow for expansion without replacing the entire unit.
- Space Optimization: Compact PDUs maximize rack or cabinet space, ensuring efficient use of available room.
- Energy Metrics: Understanding consumption patterns helps optimize power usage and reduce costs.
- Budgeting Estimations: Accurate energy consumption forecasts aid in long-term financial planning.
These considerations ensure that the chosen solution aligns with operational needs while maintaining efficiency and reliability.
When to Use a PDU
PDUs are ideal for environments requiring organized power distribution across multiple devices. Data centers benefit significantly from PDUs due to their ability to manage high-density setups.
- Horizontal rack PDUs fit seamlessly into standard racks, optimizing cable management and airflow.
- Intelligent PDUs monitor power usage and environmental conditions, enabling administrators to identify inefficiencies.
- Redundancy features ensure uninterrupted operations during maintenance or equipment failures.
PDUs excel in scenarios where scalability and flexibility are essential. Their ability to distribute power evenly prevents overloads and extends the lifespan of connected equipment.
When to Use a PSU
PSUs are indispensable for devices requiring stable and regulated power conversion. They are commonly used in computers, gaming consoles, and industrial equipment.
- Budgetary Energy Estimations: PSUs provide realistic energy consumption forecasts, aiding cost-effective decision-making.
- Expected Maximum Power Load: Determining the number of nodes a PSU can support ensures optimal performance.
PSUs are particularly effective in environments with fixed work scenarios. They complete tasks efficiently by converting high-voltage AC into low-voltage DC, ensuring consistent power delivery to sensitive components. Their built-in protection features safeguard devices against electrical faults, enhancing reliability and longevity.
PDUs and PSUs serve distinct yet complementary roles in power management.
- PDUs distribute power efficiently across devices, while PSUs convert it into usable formats for hardware.
- Together, they prevent overloads and ensure consistent energy delivery, critical for data centers.
| Trend Category | Description |
|---|---|
| AI-User Perspective | Focus on power-aware AI training and robust deployment for PDUs and PSUs. |
| Data-Center Perspective | Emphasis on AI-aware power pattern modeling and advanced cooling solutions. |
Choosing the right device depends on operational needs, scalability, and energy efficiency goals.
FAQ
What is the main difference between a PDU and a PSU?
A PDU distributes power to multiple devices, while a PSU converts electrical energy into usable formats for individual components.
Can PDUs and PSUs be used together?
Yes, they complement each other. PDUs distribute power, and PSUs convert it, ensuring reliable energy delivery in environments like data centers.
How do I choose between a PDU and a PSU?
Evaluate your needs. Use a PDU for power distribution across devices. Use a PSU for converting power within individual electronic systems.
Post time: Jun-03-2025